A cardiologist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the cardiovascular system, which includes the heart and blood vessels. Their main goal is to prevent, detect, and manage heart-related conditions through both medical and lifestyle interventions. Heart disease remains a leading cause of death globally, and seeing a cardiologist is key to protecting your heart health.
Diagnosing Heart Conditions
Cardiologists use a variety of tools and tests to diagnose heart problems, such as:
- Electrocardiograms (ECG/EKG)
- Echocardiograms
- Stress tests
- Holter monitoring
- Cardiac catheterization
These tests help assess the structure and function of the heart, detect irregular rhythms, and determine if blood flow to the heart is restricted.
Managing High Blood Pressure
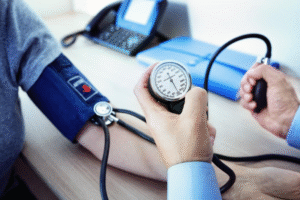
High blood pressure (hypertension) is a silent threat to heart health. A cardiologist can:
- Monitor blood pressure levels
- Adjust medications for better control
- Recommend dietary and lifestyle changes
- Prevent long-term complications like stroke or heart failure
Controlling blood pressure reduces strain on the heart and improves longevity.
Treating Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs when arteries become narrowed due to plaque buildup. Cardiologists can:
- Prescribe medications to reduce cholesterol and prevent clotting
- Monitor symptoms like chest pain (angina)
- Recommend procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery when needed
They play a vital role in preventing heart attacks through early detection and intervention.
Addressing Arrhythmias
Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) can be harmless or life-threatening. Cardiologists identify their causes and treat them using:
- Medications
- Pacemakers
- Defibrillators
- Ablation procedures
They monitor heart rhythm patterns and offer long-term management plans for safety and comfort.
Preventive Heart Care
Cardiologists help prevent heart disease in high-risk patients through:
- Regular checkups and screenings
- Risk assessments (family history, diabetes, smoking, etc.)
- Diet and exercise counseling
- Stress management strategies
Preventive care helps delay or completely avoid serious heart conditions.
Post-Heart Attack Care
After a heart attack, cardiologists guide recovery through:
- Monitoring heart function
- Prescribing rehabilitation programs
- Adjusting medications
- Providing emotional support
This phase is crucial to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of future cardiac events.
Managing Congestive Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart can’t pump blood effectively. Cardiologists help by:
- Prescribing fluid-management medications
- Recommending dietary sodium restrictions
- Tracking symptoms and progression
- Coordinating care with other specialists
Timely management improves both survival and quality of life.
Treating High Cholesterol
Elevated cholesterol contributes to artery blockages. A cardiologist can:
- Order lipid profile tests
- Prescribe statins or other cholesterol-lowering medications
- Encourage healthy eating habits and physical activity
Proper cholesterol control helps reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Monitoring Heart Valve Problems
Cardiologists evaluate heart murmurs or valve abnormalities. Common issues include:
- Aortic stenosis
- Mitral valve prolapse
- Regurgitation or insufficiency
Treatment may involve medication or referral for valve repair or replacement.
Interpreting Heart Imaging
Cardiologists analyze imaging results like:
- Cardiac MRI
- CT angiography
- Nuclear stress tests
These images provide a clearer picture of the heart’s structure and any damage or blockages, helping guide accurate treatment.
Supporting Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle is a major part of heart health. Cardiologists often help patients:
- Quit smoking
- Lose weight
- Reduce stress
- Maintain a heart-healthy diet
They create personalized wellness plans to support long-term heart function.
Educating Patients
Cardiologists explain complex medical conditions in simple terms. They ensure that patients:
- Understand their diagnosis
- Know their treatment options
- Follow through with medication schedules
- Recognize warning signs that need urgent care
Patient education empowers individuals to actively participate in their heart health journey.
Referring for Surgical Treatment
When medication and lifestyle changes aren’t enough, cardiologists refer patients to:
- Cardiac surgeons
- Electrophysiologists
- Vascular specialists
They continue to monitor the patient post-surgery and adjust care as needed.
Conclusion
Cardiologists play a crucial role in both preventing and treating heart disease. From diagnosing conditions to guiding recovery after a heart attack, they use their expertise to help patients maintain a healthy heart. Regular visits to a cardiologist, especially for those with risk factors or symptoms, can greatly improve heart function and overall well-being.
FAQs
What symptoms mean I should see a cardiologist?
Chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or irregular heartbeats are key signs that you should visit a cardiologist.
Can I visit a cardiologist even if I don’t have heart problems?
Yes, preventive visits are important—especially if you have a family history or other risk factors for heart disease.
How often should I have my heart checked?
Annually if you’re over 40 or have risk factors. Your cardiologist will suggest a schedule based on your condition.
Do cardiologists perform surgeries?
No, but they diagnose and manage heart problems and refer to cardiac surgeons when surgery is needed.
What lifestyle changes improve heart health?
A balanced diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and reducing stress all contribute to a healthier heart.