Introduction
A routine gynecological exam is an essential part of a woman’s overall health care. This annual visit helps monitor reproductive health, detect early signs of disease, and address any concerns related to the menstrual cycle, fertility, or hormonal changes. For many women, especially first-timers, understanding what to expect can ease anxiety and make the experience more comfortable.
Health History Review
The exam usually begins with a discussion about your medical history. The gynecologist will ask about:
- Menstrual cycle regularity
- Birth control use
- Sexual activity and health
- Previous pregnancies or miscarriages
- Family history of cancer or reproductive disorders
- Any current symptoms such as pain, discharge, or irregular bleeding
This information helps the doctor understand your health context and tailor the exam accordingly.
General Physical Examination
In some cases, a gynecologist may perform a brief general physical exam to assess your overall health. This can include:
- Checking your weight and blood pressure
- Examining your heart and lungs
- Evaluating thyroid function through a neck exam
Although not always part of the visit, it helps provide a holistic view of your wellness.
Breast Examination
A clinical breast exam is often included in a routine gynecological checkup. The gynecologist will manually examine your breasts and underarms for:
- Lumps or abnormal tissue
- Skin changes
- Nipple discharge
This helps in early detection of breast abnormalities or signs of cancer.
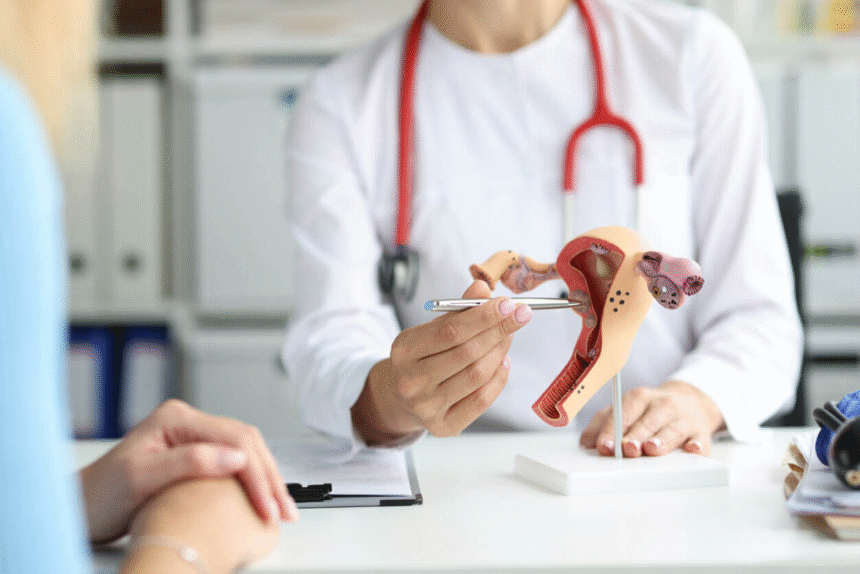
Pelvic Examination
The pelvic exam is a central part of the routine visit. It includes:
- External exam: Checking the vulva and external genitalia for signs of irritation, cysts, or abnormalities.
- Internal exam: Using a speculum to view the vaginal walls and cervix. The gynecologist looks for inflammation, lesions, or discharge.
- Bimanual exam: Inserting two fingers into the vagina while pressing on the abdomen to feel the uterus and ovaries for size, shape, or tenderness.
These steps help identify infections, fibroids, ovarian cysts, and other internal conditions.
Pap Smear (If Needed)
Depending on your age and medical history, the gynecologist may perform a Pap smear during the pelvic exam. This involves collecting a sample of cells from the cervix using a small brush. The sample is tested for:
- Abnormal or precancerous cells
- HPV (human papillomavirus), which can cause cervical cancer
This screening is crucial for early detection and prevention of cervical cancer.
STD Screening
If you’re sexually active, the gynecologist may recommend testing for sexually transmitted diseases. This can involve:
- Swabs from the cervix or vagina
- Blood or urine tests
STD screenings are confidential and essential for reproductive and overall health.
Discussion and Counseling
After the physical exams, the gynecologist will discuss the findings with you. This is also a good time to ask questions about:
- Menstrual problems
- Birth control options
- Fertility concerns
- Menopause symptoms
- Pain during intercourse
- Breast health
The doctor may offer advice on lifestyle, nutrition, and mental well-being related to women’s health.
Follow-Up and Recommendations
Based on the exam results, your gynecologist may:
- Recommend follow-up tests like ultrasound or blood work
- Suggest lifestyle changes or prescribe medications
- Schedule your next exam, typically one year later
If anything abnormal is detected, they’ll explain the next steps clearly.
Conclusion
A routine gynecological exam is a proactive step in maintaining a woman’s health. It involves reviewing medical history, performing a physical and pelvic exam, and offering screening tests like the Pap smear or STD check. These visits also provide a chance to talk openly with your doctor about any reproductive or hormonal concerns. Regular exams lead to early detection, better health outcomes, and peace of mind.
FAQs
Is a pelvic exam painful?
It might feel uncomfortable, but it shouldn’t be painful. Communicate with your doctor if you experience discomfort.
How often should I get a Pap smear?
Most women should have one every 3 years starting at age 21, but your doctor may adjust this based on your history.
Do I need to shave or prepare before a gynecology visit?
There’s no need to shave or do anything special. Just maintain normal hygiene.
Can I see a gynecologist if I’m not sexually active?
Yes, gynecological exams are important for all women, regardless of sexual activity.
What should I do if I feel nervous?
It’s completely normal. Let the doctor know—gynecologists are trained to make you feel comfortable and respected.