Bunions are a common foot condition that can lead to discomfort and challenges when wearing shoes or walking. These bony bumps range in severity and require prompt treatment. Here are a few common questions about bunions, focusing on their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options:
What Are Bunions?
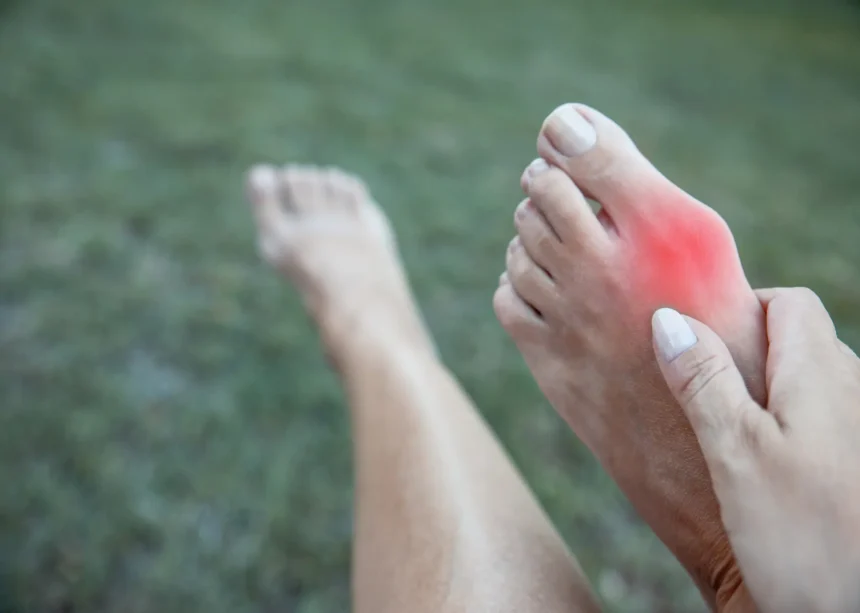
Bunions are a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe. Over time, the big toe pushes against the adjacent toes, causing the joint to misalign and enlarge. The foot’s natural shape changes as the bunion increases in size, potentially leading to noticeable swelling and discomfort around the affected area.
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role; individuals with a family history of bunions are more likely to experience them. Foot mechanics, such as flat feet, low arches, or excessive pronation, can also accelerate their formation. Wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, particularly those with narrow toe boxes or high heels, adds pressure to the big toe joint. This consistent pressure can exacerbate misalignment over time.
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of bunions vary depending on their severity. Common signs include a visible bump on the side of the foot at the base of the big toe. Swelling, redness, or tenderness may develop around this area, particularly after prolonged standing or walking. Some individuals experience discomfort or pain that worsens with certain activities or when wearing restrictive footwear.
Changes in the alignment of the toes often accompany the bunion as the big toe may angle toward other toes, sometimes overlapping them. Advanced bunions can lead to additional complications. Calluses or corns may form where the toes rub against one another or the inside of a shoe. Joint stiffness and reduced mobility in the big toe are also possible, especially as the bunion progresses.
How Are They Treated?
Treatment options for bunions are determined by their severity and the level of discomfort they cause. Non-surgical methods are often effective for managing symptoms and slowing progression. These include wearing shoes with a wide toe box to alleviate pressure on the joint, using orthotic inserts to improve foot alignment, and applying padding to protect the bunion from friction. Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications may reduce pain and swelling.
For more advanced bunions that significantly affect mobility or cause persistent pain, surgical intervention may be necessary. Bunion surgery, or bunionectomy, involves realigning the joint and removing excess bone. The type of surgical procedure depends on the bunion’s severity and the individual’s specific condition. Recovery generally includes a period of limited weight-bearing, followed by physical therapy to restore mobility and strength in the foot.
Find a Podiatrist
Bunions are a common condition involving a misalignment of the big toe joint, often caused by genetic factors, poor footwear, or irregular foot mechanics. Symptoms range from visible bumps and mild discomfort to significant pain and joint stiffness. While non-surgical approaches can alleviate symptoms and prevent worsening, surgical options effectively address severe cases.
If you experience persistent discomfort or difficulty walking, consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate approach for management or treatment. Addressing the condition early can provide relief and improve your quality of life.