Arthritis is a common condition that causes joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Orthopedic surgeons specialize in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions, including various forms of arthritis. They offer both surgical and non-surgical treatment options designed to relieve pain, restore function, and improve quality of life. Recognizing the signs that indicate you need specialized care can help you take proactive steps toward better joint health.
What Is an Orthopedic Surgeon?
An orthopedic surgeon is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system. This includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. These specialists possess comprehensive knowledge of both surgical and non-surgical treatment methods. Their expertise extends beyond surgery to include injury prevention, rehabilitation guidance, and long-term management strategies for chronic conditions like arthritis.
What Is Arthritis?
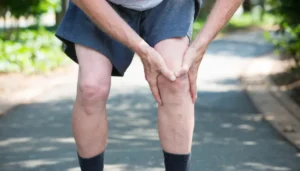
Arthritis is a general term describing inflammation of one or more joints. This condition affects the cartilage, the smooth tissue that covers the ends of bones where they meet to form joints. When cartilage breaks down or becomes inflamed, it can cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion in the affected joints.
There are over 100 different types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the most common forms. Osteoarthritis occurs when cartilage wears down over time, typically affecting weight-bearing joints such as knees, hips, and spine. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
What Are the Causes and Symptoms?
Multiple factors contribute to arthritis development. Age represents the most significant risk factor, as cartilage naturally deteriorates over time. Genetics also plays a role, with family history increasing the likelihood of developing certain types of arthritis. Previous joint injuries, whether from sports, accidents, or repetitive stress, can predispose joints to arthritic changes later in life.
Common symptoms of arthritis include persistent joint pain that may worsen with activity or weather changes. Stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity, may accompany the pain. Swelling around affected joints, reduced range of motion, and a grinding sensation during movement are additional indicators.
How Is Arthritis Treated?
Arthritis treatment typically follows a progressive approach, beginning with conservative methods before evaluating more invasive interventions. Physical therapy represents a cornerstone of arthritis management, focusing on maintaining joint mobility, strengthening surrounding muscles, and improving overall function. Bracing and compression devices provide external support to affected joints, reducing stress and pain during daily activities.
Immobilization techniques, such as splinting, may be recommended during acute flare-ups to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Anti-inflammatory injections offer targeted relief for specific joints. These treatments can delay the need for surgical intervention while maintaining quality of life.
Surgery becomes an option when conservative treatments no longer provide adequate relief. Arthroscopic procedures can remove damaged cartilage or bone spurs, while joint replacement surgery may be recommended for severely damaged joints. The decision to pursue surgical treatment depends on factors such as pain level, functional limitation, and overall health status.
Consult a Surgeon Today
Understanding arthritis and the role of orthopedic surgeons in its treatment helps patients make informed decisions about their care. Early intervention can slow disease progression and preserve joint function for longer periods. If you’re experiencing persistent joint pain, stiffness, or reduced mobility that interferes with daily activities, consult an orthopedic surgeon. These specialists can provide an accurate diagnosis, develop personalized treatment plans, and guide you through both non-surgical and surgical options as needed.