An ankle sprain is a common injury, often causing pain, swelling, and difficulty walking. When the discomfort doesn’t improve with rest or home care, a visit to a podiatrist can provide the answers and treatment needed for proper healing. Knowing what to expect helps patients feel prepared and makes sure they receive the right care to restore mobility. Here’s what you can expect from a visit to he podiatrist for ankle pain:
Initial Evaluation and Medical History
Your first appointment for ankle pain will begin with an initial evaluation. The podiatrist will ask questions about your medical history and the specifics of your injury. You should be prepared to discuss when the ankle pain started, what you were doing when the injury occurred, and if you heard a popping sound. The podiatrist will ask about the type of pain you are feeling, whether it is sharp, dull, or aching. Providing detailed information about previous ankle injuries is also helpful for understanding your overall health.
Physical Examination of the Ankle
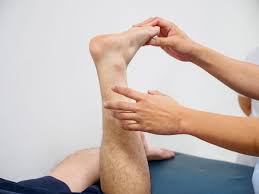
After reviewing your medical history, the podiatrist will perform a physical examination of your sprained ankle. This hands-on assessment is a key part of the diagnostic process. The podiatrist will carefully inspect your ankle, foot, and lower leg for any visible signs of injury, such as swelling, bruising, or deformities. This visual check helps to gauge the severity of the ankle sprain.
The examination also involves the podiatrist gently pressing on different areas around your ankle to pinpoint sources of tenderness or warmth. This helps identify the specific ligaments that are damaged. To assess your ankle’s stability and range of motion, the specialist will move your foot carefully in various directions. While this may cause some discomfort, it provides valuable information about the extent of damage.
Diagnostic Tests for Accurate Results
In some cases, a physical examination alone may not be sufficient for a definitive diagnosis. Your podiatrist may recommend diagnostic imaging to get a clearer view of the structures inside your ankle. These tests are useful for ruling out other potential issues, like fractures, and for determining the precise level of ligament damage. Common diagnostic tests for ankle pain include:
- X-rays: These images can reveal bone fractures or dislocations that may have occurred along with the ankle sprain.
- MRI Scans: An MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues, including ligaments, which is valuable for assessing the severity of a tear.
- CT Scans: A CT scan creates cross-sectional images of the ankle, offering a detailed look at the bones and joints.
These diagnostic tools are fundamental for identifying the underlying cause of ankle pain and guiding the development of an effective treatment plan.
Guidance on Treatment and Recovery
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, your podiatrist will develop a personalized treatment plan for your ankle sprain. The goal is to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing, and restore function. The recommended treatment will depend on the severity of your injury. For mild ankle sprains, conservative methods are often effective.
These may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (the RICE method). The foot specialist may also recommend anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain and swelling. Physical therapy exercises may also be recommended to regain strength and stability
For severe injuries, your podiatrist may suggest other treatments. This may include custom orthotics for support or injections to reduce inflammation. The specialist will explain each treatment option and guide you through each stage of your recovery.
Treat your ankle sprain today.
Understanding the process of a podiatrist visit for a sprained ankle can help you feel prepared for your appointment. From the initial evaluation to the final treatment plan, each step is designed to provide an accurate diagnosis and guide you toward a full recovery. For persistent ankle pain or ankle sprain, contact a podiatrist near you to schedule a consultation for addressing your symptoms.