Ingrown toenails may start as a minor irritation but can quickly develop into pain, swelling, and infection if not addressed promptly. Recognizing the early signs of ingrown nails is key to preventing complications and seeking timely treatment. By learning what to watch for and how to respond, individuals can protect their foot health and prevent future problems. Here’s more information on how to spot an ingrown toenail before it gets worse:
Identifying Causes of Ingrown Nails
Ingrown toenails can develop due to various factors, many of which are preventable with proper care. Common causes include:
- Improper Nail Trimming: Cutting nails too short or rounding the edges can encourage the nail to grow into the skin.
- Ill-fitting Footwear: Shoes that are too tight or narrow can place excess pressure on the toes, increasing the risk of ingrown nails.
- Trauma to the Toenail: Injuries, such as stubbing a toe or repeated pressure from activities like running, can lead to nail growth abnormalities.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have naturally curved toenails, making them more prone to ingrown toenails.
- Poor Foot Hygiene: Failure to keep the feet clean and dry create an environment conducive to the development of this condition.
By understanding these contributing factors, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing ingrown toenails and maintain better overall foot health.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
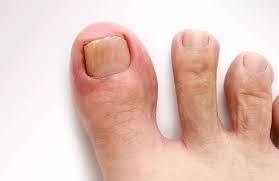
The early signs of an ingrown toenail often include tenderness, swelling, and redness around the affected nail. These symptoms begin at the corner or side of the toenail where the nail starts to grow into the surrounding skin. Pain may be noticeable when pressure is applied, such as while wearing shoes or walking. The skin may also appear inflamed due to irritation caused by the embedded nail.
If left untreated, these signs progress and lead to severe complications. The nail may break the skin, allowing bacteria to penetrate and cause an infection. Signs of an infected ingrown toenail include increased pain, significant swelling, and the presence of pus. In some cases, the infection may spread, resulting in a severe condition. Prompt identification and intervention are key to preventing worsening and the need for invasive treatments.
Preventing and Treating Ingrown Nails
Taking proactive steps can help prevent ingrown toenails or complications from developing. Follow these guidelines for effective prevention and treatment:
- Trim your toenails properly: Cut your toenails straight across and avoid rounding the edges to prevent them from growing into the skin.
- Ensure proper footwear: Wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate space for your toes, avoiding pressure or crowding.
- Maintain good foot hygiene: Wash your feet regularly and keep them dry to reduce the likelihood of infections.
- Monitor your feet closely: Check for early signs, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness around the edges of the nail.
- Use appropriate foot protection: Avoid injuries by wearing protective footwear in situations where your toes are at risk of trauma.
- Seek medical assistance when needed: If you experience persistent pain, signs of infection, or recurrent ingrown toenails, consult a podiatrist for professional care.
By following these preventative measures and addressing issues promptly, you reduce the likelihood of complications and maintain healthy feet.
Get Help for Ingrown Toenails
Recognizing the early symptoms of ingrown toenails is the first step toward preventing pain and infection. By understanding the causes and implementing preventative measures, you can maintain healthy feet. For signs of an infection or persistent toe pain, contact a trusted podiatrist near you for proper evaluation and treatment.