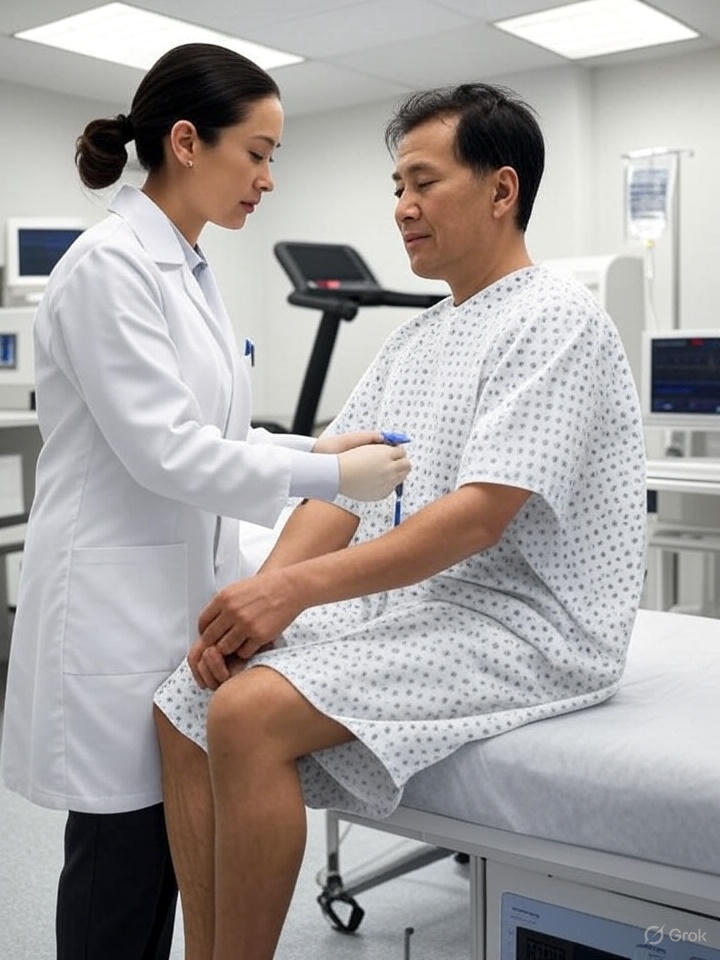
A nuclear stress test is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle. During the test, a small, safe amount of a radioactive substance, called a tracer, is typically injected into your bloodstream. This allows your healthcare provider to observe how well blood is reaching different parts of your heart, providing a detailed picture of its function. Here is more information about what nuclear stress testing results might mean:
Restful and Active Stages
The nuclear stress test unfolds in two distinct phases. The first is the restful stage. During this part, you will lie down so the radioactive tracer can be administered through an IV. After allowing some time for the tracer to circulate and be absorbed by the heart muscle, the camera can take a set of images. These pictures show the blood flow to your heart when it is not working hard.
The second phase of nuclear stress testing is the active or stress stage. To stress your heart, you may walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike. The intensity will gradually increase, increasing your heart rate.
If you are unable to exercise, a medication can be given through your IV. This can simulate the effects of exercise on your heart. At the point of peak stress, another dose of the tracer is typically injected, and a second set of images is taken. Comparing the restful and active images helps identify areas of the heart that may not be receiving adequate blood flow under stress.
Normal Results
Receiving normal results from a nuclear stress test indicates that there is consistent and even blood flow to all parts of your heart muscle. This means the results were normal during both the rest and stress portions of the test. The radioactive tracer appears to have been distributed uniformly throughout the heart in both sets of images. Your doctor may review these findings with you and discuss their implications for your overall heart health.
Abnormal Results
An abnormal stress test result suggests there may be an issue with blood flow to your heart. A reversible defect occurs when blood flow appears normal at rest but is reduced during the stress phase. This pattern often points to a narrowed or blocked coronary artery that restricts blood flow when the heart needs it most, such as during physical activity.
A fixed defect means there is a lack of blood flow to a part of the heart during both the rest and stress images. This usually indicates an area of the heart muscle that has been permanently damaged. Doctors typically document the size and location of any blood flow defect in the report. This information helps your doctor determine the extent of the problem. It also helps them decide on the next steps for your care plan.
Inconclusive Results
Sometimes, the results of a nuclear stress test are unclear. This outcome does not necessarily point to a specific problem with your heart. Instead, it means the images obtained were not clear enough to make a definitive diagnosis.
Schedule Nuclear Stress Testing
Understanding the information from a nuclear stress test provides a clearer view of your heart’s function. The results guide your healthcare provider in creating a personalized approach to your health. If you have questions about your heart or believe you could benefit from this type of evaluation, the next step is to speak with a professional. Contact a clinic today to schedule a consultation with one of our cardiologists.