Athletic injuries can disrupt the lives of individuals who engage in physical activity, presenting distinct medical and rehabilitative challenges. The specialty of sports medicine focuses on meeting these challenges with approaches uniquely suited to restore function and support ongoing participation in exercise or sport. This field draws on expertise in biomechanics and musculoskeletal medicine to help athletes and active individuals recover from injury and reduce the likelihood of further harm.
What Is Sports Medicine?
Sports medicine specializes in the care of injuries and issues related to physical activity and sports participation. It brings together a team of professionals who coordinate to address patient needs through both preventive and direct treatment. Training in this field of medicine includes an in-depth study of musculoskeletal injuries, movement analysis, and the impact of exercise on the body. This specialty addresses immediate physical trauma as well as underlying factors, focusing on patient-centered, evidence-based care.
What Injuries Can It Treat?
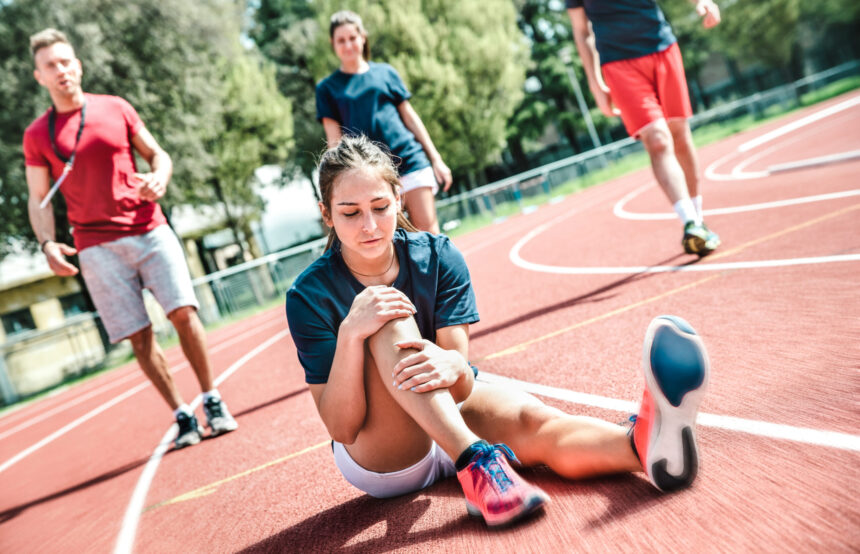
Sports medicine treats a range of acute and overuse injuries associated with athletics. Acute injuries, such as sprains, strains, and fractures, often result from direct impacts or abrupt changes in movement. These events can damage joints like the knee or shoulder, cause ligament tears, and lead to further joint complications. Repetitive activity may produce overuse conditions, including tendinitis, stress fractures, and joint problems. Athletes can report injuries like tennis elbow or runner’s knee, which are addressed with targeted strategies grounded in both prevention and recovery.
Muscle and tendon injuries, ranging from mild strains to severe ruptures, are frequent in physically active groups. This includes injuries to the hamstring, calf, and Achilles tendon. Recognizing and managing these injuries promote safety and help guide return-to-play decisions.
How Does It Treat Them?
Sports medicine treatments are informed by comprehensive assessment and diagnosis, using examination and imaging to guide decisions. Care providers may use a range of methods to locate the source of a sports injury. This can include lab work such as blood tests and imaging techniques such as X-rays and ultrasound.
Non-surgical treatments are widely used and focus on rest, structured activity modification, and injury-specific protocols to manage symptoms and encourage healing. Physical therapy forms the core of most recovery plans, with therapeutic exercise restoring function, mobility, and strength. Other forms of therapy, such as manual techniques and monitored rehabilitation programs, can be employed to address pain, support recovery, and safely increase activity levels. More advanced modalities may be explored, including corticosteroid injections, when appropriate for particular injuries.
Recovery in sports medicine always emphasizes careful progression back to previous activity levels. Individualized rehabilitation programs account for tissue healing rates and biomechanical corrections. Prevention strategies are closely integrated and can focus on strengthening, improving flexibility, and refining movement patterns to decrease the likelihood of future injury. Nutritional support and guidance around rest may add further support to the recovery process.
Seek Professional Medical Expertise
Injuries that occur during sport and exercise often require specialized care tailored to the physical demands of active individuals. Sports medicine professionals collaborate to develop treatment plans that address immediate recovery and long-term goals, supporting a safe return to activity. Timely evaluation and intervention may help shorten recovery time and reduce the risk of recurring issues.