Vein care focuses on diagnosing and managing vein disorders that impact the body’s circulation. Healthy veins carry blood from the body back to the heart. When veins do not work as they should, symptoms such as swelling and an increased risk of blood clots can develop. Here is more information on how vein health relates to these problems, how providers diagnose vein disorders, and common strategies for managing them:
Understanding Venous Insufficiency
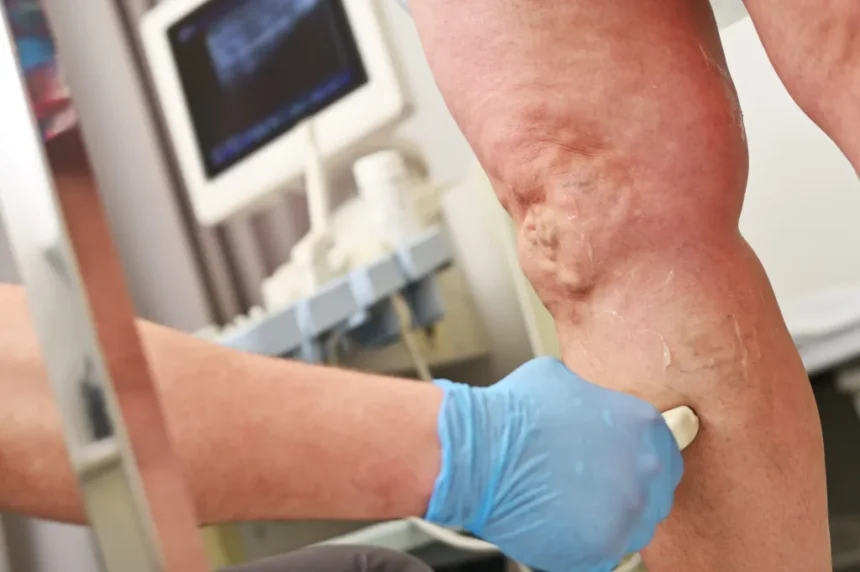
Vein care focuses on the venous system, which brings oxygen-poor blood from the body back to the heart. In the legs, veins contain one-way valves that allow blood to move upward against gravity. If these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can collect in the legs rather than flow upward as it should. This pooling, called venous stasis, often leads to swelling.
Extra pressure from pooled blood can push fluid out of the veins into nearby tissues, which causes swelling, or edema. Venous stasis also raises the risk of developing blood clots. One type, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), forms in a deep leg vein. If the clot travels to other parts of the body, it can create further complications.
Evaluating for Vein Conditions
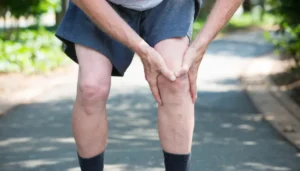
Diagnostic evaluation begins with a healthcare provider gathering information about symptoms and health history. The provider asks about experience with swelling, aching, skin changes, or a sense of heaviness in the legs. A detailed physical exam follows. The provider reviews the legs for signs of vein disease, including visible veins, discoloration, or skin ulcers.
Duplex ultrasound is a standard, noninvasive tool to assess veins. It creates images of the veins while also showing blood movement and direction. With this scan, a provider can locate damaged valves and observe how well blood flows through the veins. The ultrasound also helps reveal any blood clots. All of this information guides the provider in developing an individualized treatment plan.
Managing Venous Issues
Vein care often includes a combination of strategies aimed at improving circulation and controlling symptoms. Compression therapy is a first-line approach for many patients and applies firm, even pressure to the legs. This support helps veins move blood upward and reduces pooling, which can help decrease swelling.
Lifestyle adjustments also contribute to better vein health. Walking and other physical activities engage leg muscles, which assist in pumping blood back to the heart. Raising the legs above the level of the heart periodically during the day allows gravity to further support blood flow out of the legs, helping minimize swelling. In some cases, procedure-based treatments address problem veins directly. These procedures can close off or remove unhealthy veins, guiding blood flow into healthier veins.
Get Vein Care
Vein care targets conditions that can cause swelling and increase the risk of blood clots in the legs. When valves in the veins lose function, blood pools and pressure rises, leading to these symptoms. Healthcare providers rely on thorough clinical assessments and duplex ultrasound to diagnose vein problems accurately. Management includes compression therapy, lifestyle changes such as exercise and leg elevation, and sometimes minimally invasive vein procedures. By supporting proper vein function, these strategies help manage symptoms and support overall circulation.