Regenerative medicine is a medical field that aims to repair, replace, or regenerate damaged tissues or organs. Stem cell therapy is utilized for its potential to support tissue repair and the natural healing process. This therapy is actively studied and remains under ongoing scientific evaluation for its use in regenerative medicine.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
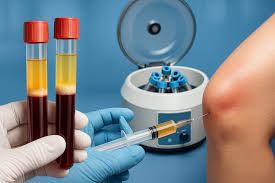
Stem cell therapy involves the use of cells with the ability to develop into different types of tissue. These undeveloped cells can self-renew and may change, or “differentiate,” into specialized cells. The method of stem cell collection depends on the cell source. Once collected, stem cells are processed in a laboratory to be prepared for use. Delivery of stem cells is determined by the targeted tissue. The cells may be injected directly into a tissue, such as a joint. Some therapies focus on autologous use, where a patient’s own cells are returned to their body.
What Does It Treat?
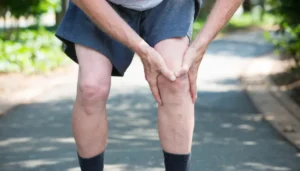
Not all applications of stem cell therapy offer established clinical benefit. Research is ongoing to determine the outcomes, best protocols, and longer-term effects of these therapies. Stem cell injections are under continued study for their potential in managing joint and soft tissue injuries.
Stem cells and their applications are primarily studied for use in certain orthopedic conditions, including joint issues such as osteoarthritis and soft tissue injuries, such as tendon or ligament problems. Research is ongoing to evaluate stem cells and similar regenerative treatments for these musculoskeletal concerns. The therapy is not universally established for all possible uses, and clinical evidence continues to evolve regarding its effectiveness and optimal treatment practices.
What Should You Expect?
A typical treatment process begins with a medical assessment. A healthcare provider reviews the individual’s medical history and completes a physical exam. Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays, may be ordered to evaluate the targeted problem. If therapy is pursued, stem cells are collected from the most suitable source, typically bone marrow, adipose tissue (also known as fat tissue), or umbilical cord tissue. Collected samples are processed to prepare the stem cells for administration.
Stem cells are administered using standard methods, such as injection into a specific joint or soft tissue, or through IV administration for systemic effects. These procedures are usually performed in a clinical setting. After injection, many patients return home the same day. Soreness or bruising may occur at the harvest or injection site. Patients generally follow a recovery or monitoring plan, which may include follow-up visits to document progress. Available stem cell therapies differ according to local regulations and medical practice guidelines. In certain regions, specific stem cell treatments may be restricted to participation in registered clinical trials.
Seek Professional Naturopathic Care
Anyone interested in exploring stem cell therapy should consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and to discuss potential approaches and alternatives available for their condition. Naturopathic doctors trained in regenerative therapies can help explain regenerative practices, describe what patients may experience during the treatment process, and support patients with evidence-based recommendations. Professional guidance enables patients to make informed decisions about their medical care.