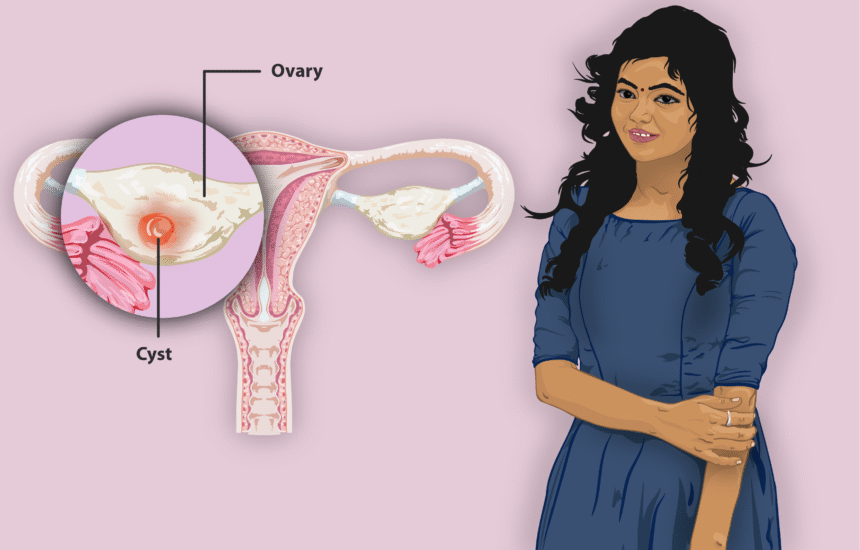
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within an ovary and are treated by an OBGYN. They are common, and many individuals with ovaries will develop at least one during their lifetime. Here is more information on what ovarian cysts are, their common symptoms, and general approaches to their management:
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
An OBGYN treats ovarian cysts, which are formations that can appear on the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. The most prevalent types are functional cysts, which develop during the menstrual cycle. These include:
- Follicular Cysts: During a menstrual cycle, an egg grows in a sac called a follicle. Typically, this follicle breaks open and releases an egg. If the follicle does not rupture, the fluid inside can form a cyst on the ovary.
- Corpus Luteum Cysts: After the follicle releases its egg, it shrinks into a mass of cells called the corpus luteum. If this sac does not shrink and instead seals, fluid can build up inside, causing a corpus luteum cyst.
Functional cysts are generally harmless, rarely cause pain, and often disappear on their own within two to three menstrual cycles. Other, less common types of cysts can also form. These include dermoid cysts, cystadenomas, and endometriomas. While most ovarian cysts are benign and noncancerous, a small percentage may be malignant.
Exploring Common Symptoms
Many ovarian cysts do not produce any symptoms and are discovered during a routine pelvic exam. When symptoms do occur, they can include pelvic pain, which may be a dull ache or a sharp pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst. This pain can be constant or intermittent.
Other signs may include a feeling of fullness or heaviness in the abdomen and bloating. Some individuals might experience pain during intercourse or during bowel movements. A large cyst can press on the bladder, causing a frequent or urgent need to urinate. In the event of a cyst rupturing, it can cause sudden, severe pain.
Managing Ovarian Cysts
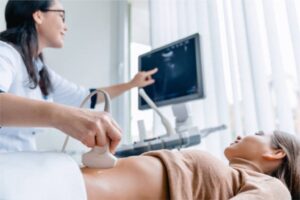
The management strategy for an ovarian cyst depends on its type, its size, the symptoms it causes, and the individual’s age. A healthcare provider will evaluate these factors to determine the appropriate course of action. For many simple, functional cysts, a period of watchful waiting is a common approach. This involves monitoring the cyst over a few weeks or months with follow-up pelvic ultrasounds to see if it changes in size or resolves on its own. During this time, pain relievers may be suggested for any discomfort.
For cysts that are large, persistent, or cause significant symptoms, other interventions may be discussed. Hormonal medications, such as birth control pills, can sometimes be prescribed to help prevent the formation of new cysts. In cases where a cyst is suspicious for malignancy or is causing severe pain, a surgical procedure to remove the cyst may be recommended.
Find an OBGYN
This article offered a look at ovarian cysts, their common symptoms, and typical management approaches. We defined what ovarian cysts are, noting that functional cysts are the most common type. We also detailed symptoms such as pelvic pain and bloating, and outlined management strategies ranging from watchful waiting to surgical intervention. If you think you have an ovarian cyst, consult with an OBGYN to learn more.