Skin conditions affect people of all ages and can range from mild to severe. Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating these issues to improve comfort, appearance, and overall health. Understanding the most common skin conditions can help individuals recognize symptoms early and seek professional care when needed.
Acne
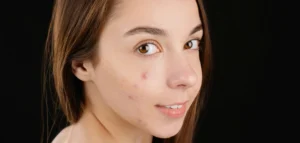
Acne is the most frequent reason people visit a dermatologist. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. Common types include:
- Blackheads and whiteheads
- Pimples and pustules
- Cystic acne
Acne affects teenagers the most but can persist into adulthood. Treatment options include topical creams, oral medications, and lifestyle changes.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is a chronic condition that causes:
- Itchy, inflamed skin
- Redness and dryness
- Cracked or rough patches
It often starts in childhood but can continue into adulthood. Dermatologists may prescribe moisturizers, steroid creams, or immune-modulating treatments to manage flare-ups.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that leads to rapid skin cell turnover, causing:
- Thick, red patches
- White or silvery scales
- Cracking and bleeding skin
It often affects the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Treatments include topical ointments, phototherapy, and biologic drugs.
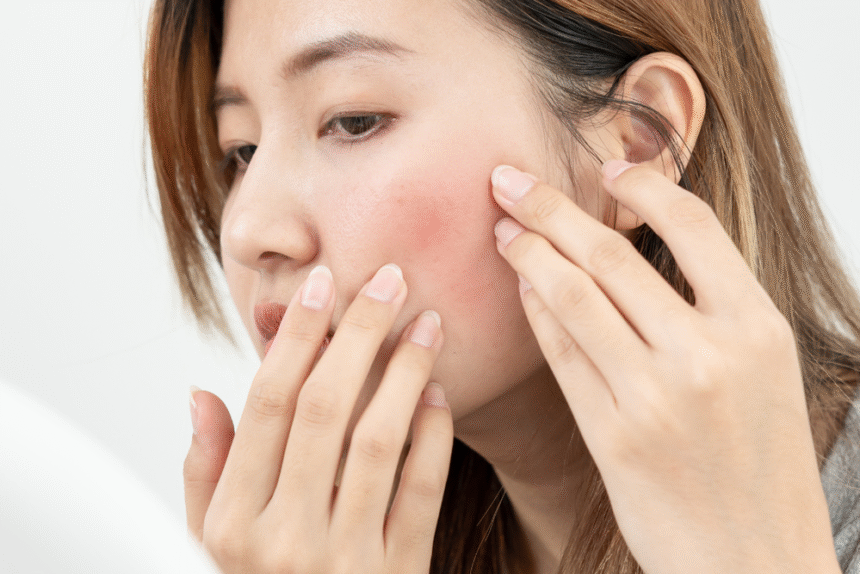
Rosacea
Rosacea causes facial redness and visible blood vessels. In some cases, it leads to:
- Acne-like bumps
- Eye irritation
- Thickened skin on the nose
Common triggers include spicy foods, heat, and stress. Dermatologists often recommend topical creams, oral antibiotics, or laser therapy.
Fungal Infections
Fungal skin infections like ringworm, athlete’s foot, and jock itch are also common. Symptoms include:
- Red, scaly, or itchy patches
- Peeling or cracking skin
- Circular rashes
These infections spread easily and are treated with antifungal creams or oral medications.
Warts
Caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), warts are small, rough skin growths. They can appear on:
- Hands and fingers
- Feet (plantar warts)
- Face or genitals
Dermatologists remove them using freezing (cryotherapy), laser treatment, or topical solutions.
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives are raised, red welts on the skin caused by allergic reactions or unknown triggers. They may:
- Appear suddenly
- Itch or sting
- Disappear within hours or days
Chronic hives may need antihistamines, corticosteroids, or allergy testing by a dermatologist.
Contact Dermatitis
This occurs when the skin reacts to an irritant or allergen. It causes:
- Redness and inflammation
- Itching or burning
- Blistering in severe cases
Common culprits include soaps, detergents, or metals like nickel. Dermatologists diagnose it through patch testing and prescribe soothing treatments.
Skin Cancer
Dermatologists frequently diagnose skin cancers such as:
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
These cancers may start as unusual moles, lumps, or discolored patches. Early detection through skin exams and biopsies improves treatment outcomes dramatically.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
This causes flaky, greasy scales and redness, especially:
- On the scalp (dandruff)
- Around the nose and eyebrows
- Behind the ears
It’s common in infants (cradle cap) and adults. Treatment includes medicated shampoos and anti-inflammatory creams.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo leads to loss of pigment, creating white patches on the skin. It is caused by immune cells attacking pigment-producing cells.
While not painful, it can impact self-confidence. Dermatologists offer light therapy, topical treatments, and cosmetic cover-ups.
Hyperpigmentation
This condition involves dark patches caused by:
- Sun exposure
- Hormonal changes
- Skin injuries or inflammation
Melasma is a common form, especially in pregnant women. Dermatologists use peels, lasers, and creams with ingredients like hydroquinone or retinoids.
Cold Sores (Herpes Simplex Virus)
Cold sores are painful, fluid-filled blisters near the lips or nose. Triggered by stress, illness, or sun exposure, they typically heal in 7–10 days. Antiviral medications can speed recovery and reduce outbreaks.
Alopecia (Hair Loss)
Hair loss may be due to genetics, autoimmune disease, or stress. Common types include:
- Androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness)
- Alopecia areata (patchy hair loss)
- Telogen effluvium (stress-related shedding)
Dermatologists determine the cause and recommend treatments such as minoxidil, steroid injections, or hair transplants.
Nail Disorders
Conditions like nail fungus, discoloration, or pitting may indicate deeper health problems. Dermatologists evaluate nail health and prescribe antifungal or corrective treatments.
Conclusion
Dermatologists play a critical role in identifying and treating a wide range of skin conditions. From acne to skin cancer, their expertise ensures accurate diagnosis and effective care. If you notice persistent skin issues or changes, consulting a dermatologist can help you manage the condition and maintain healthy skin.
FAQs
What is the most common skin problem dermatologists treat?
Acne is the most common reason people visit dermatologists.
Can dermatologists treat hair and nail problems?
Yes, dermatologists also specialize in disorders of the hair and nails.
When should I see a dermatologist?
If you have skin changes, persistent rashes, unusual moles, or acne that doesn’t improve with OTC products.
Are skin conditions contagious?
Some are, like fungal infections and warts, while others (e.g., psoriasis or eczema) are not.
Is it safe to treat skin conditions at home?
Mild issues may be managed at home, but persistent or worsening conditions should be seen by a dermatologist.