Introduction
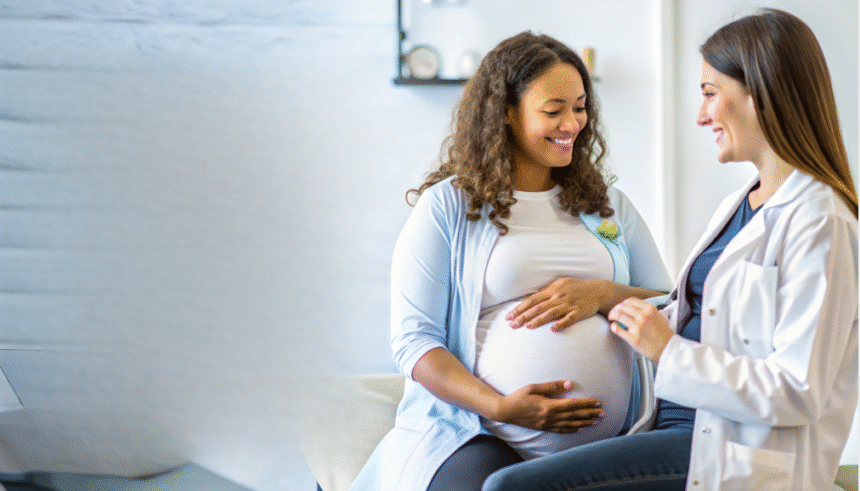
Pregnancy is a life-changing journey that requires medical support, emotional reassurance, and continuous monitoring. A gynecologist plays a central role in this process, from confirming pregnancy to delivery and postpartum care. These specialists ensure both mother and baby remain healthy, provide guidance at every stage, and address complications that may arise. Their expertise is critical to achieving a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Confirming and Monitoring Early Pregnancy
Gynecologists begin by confirming pregnancy through:
- Blood or urine tests to detect hCG hormone
- Ultrasound to visualize the gestational sac and heartbeat
- Physical exam to assess uterus and cervix
They estimate gestational age and calculate the due date. Early visits also include advice on lifestyle, diet, supplements (especially folic acid), and managing morning sickness.
Routine Prenatal Checkups
Throughout the pregnancy, a gynecologist provides regular checkups to:
- Monitor baby’s growth and heart rate
- Check maternal weight, blood pressure, and overall health
- Conduct ultrasounds at key stages (e.g., 12, 20, and 32 weeks)
- Screen for gestational diabetes, anemia, or infections
- Detect signs of complications like preeclampsia
Prenatal visits typically occur every 4 weeks in the first 28 weeks, every 2 weeks until week 36, and weekly after that until delivery.
Addressing Pregnancy Symptoms and Discomforts
Gynecologists help manage common pregnancy symptoms such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Back pain and pelvic pressure
- Heartburn and constipation
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood swings
They offer advice on safe medications, physical exercises, and healthy routines to ease discomfort without harming the baby.
Managing High-Risk Pregnancies
Some women face high-risk pregnancies due to factors like:
- Advanced maternal age
- Diabetes or hypertension
- Multiple pregnancies (twins/triplets)
- History of miscarriage or complications
Gynecologists monitor these pregnancies more closely, often in collaboration with maternal-fetal medicine specialists. Extra scans, lab work, and treatment adjustments are done to ensure safety.
Preparation for Labor and Delivery
In the final trimester, gynecologists:
- Discuss birth plan options (vaginal vs. cesarean)
- Educate the mother on signs of labor
- Monitor fetal positioning
- Evaluate readiness for delivery
They also prepare the patient for possible induction, epidural options, or emergencies during childbirth.
Performing the Delivery
Gynecologists oversee the entire labor process. During delivery, they:
- Monitor the baby’s heart rate
- Ensure safe progress of labor
- Perform episiotomy or C-section if needed
- Deliver the baby and placenta safely
Their quick decision-making is vital during emergencies, ensuring the best outcomes for mother and child.
Postpartum Care
The role doesn’t end at childbirth. Gynecologists:
- Examine the mother for healing and infections
- Support emotional health and screen for postpartum depression
- Advise on breastfeeding and birth control
- Provide recovery tips and follow-up plans
A typical postpartum checkup is done around 6 weeks after delivery, but additional visits may be scheduled as needed.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Pregnancy is both joyful and overwhelming. Gynecologists offer more than just medical care. They:
- Listen to the mother’s concerns
- Educate partners and families
- Encourage confidence and healthy choices
Their emotional support reduces anxiety and enhances the pregnancy experience.
Conclusion
Gynecologists are essential partners in pregnancy care. They guide, protect, and support women from conception to childbirth and beyond. With their medical expertise and compassionate care, mothers can enjoy a healthier, safer pregnancy journey.